The word “color gamut” is separated into two words: color is the color of the tft display screen, and domain is the space and range. The two words together mean the range of color space of the display, which represents the specific situation of a color image can show color. The wider the color gamut can display more colors, the more the human eye will see the richer and more realistic picture.
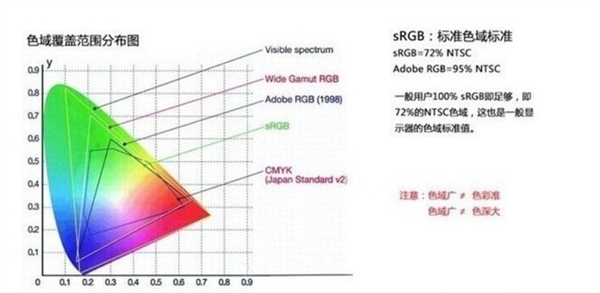
The color gamut space corresponds to different usage scenarios, and the most common one in our daily life is the sRGB color gamut. When the sRGB gamut value is 100%, it means that the monitor can display all the colors in the sRGB gamut space.
Adobe RGB color gamut, on the other hand, is a professional color gamut standard developed with photography technology. This color gamut has a wider color space than sRGB, and it contains a CMYK color gamut that is not available in sRGB, with richer levels. For professional users in the fields of printing, photography, and design, a monitor with a broader coverage of Adobe RGB color gamut is more appropriate.
NTSC color gamut is a color gamut space standard developed by the U.S. Television Standards Committee, which is wider than sRGB and Adobe RGB, both of which are used mainly for wide color gamut TV standards, and some very professional wide color gamut monitors also use it as a color gamut standard.
In is that there is also a DCI-P3 color gamut. This is the RGB color space common in American digital movies, which is the standard for Hollywood movies, so it is also known as the cinematic color gamut.
Through the previous knowledge understanding, we know that the color gamut has many standards according to different application scenarios, and the size of the color space varies from standard to standard.
The display covers 72% NTSC color gamut, which is equivalent to 100% sRGB color gamut of the screen color. In fact, from the color gamut space alone, 100% sRGB gamut is indeed equivalent to 72% NTSC color gamut space. However, 72% of the gamut space cannot be simply converted to 100% of the sRGB gamut.
72% NTSC is a comparison of the actual colors displayed by the monitor with the standard NTSC color gamut space, where each color can be displayed in a different color gradation, but together they cover 72% of the NTSC color gamut.
For example, a monitor that can fully display the NTSC gamut blue color, if his color gamut measured out to be 72% NTSC, then it must be bad to display other colors. And this monitor may not be able to cover 100% of the sRGB gamut for colors other than blue.
Suppose, say 100% of the sRGB gamut is 6 blues, 6 yellows, and 6 blacks. But the monitor can actually display 15 kinds of blue, 3 kinds of yellow, and 4 kinds of black. Then, the display shows 3 more colors than 100% sRGB gamut, which is 116% sRGB. But in reality, a monitor that can only display 3 kinds of yellow and 4 kinds of black is definitely not able to achieve 100% sRGB color gamut.
1. Use CA310 to measure the brightness of the display backlight. This determines whether the display complies with specified brightness standards, such as NITS or CD/m², etc.
2. Use a professional color calibration instrument, such as Datacolor Spyder or X-Rite i1, to calibrate the color of the display. These instruments ensure the color accuracy and consistency of the monitor.
3. Use test images, such as brightness and contrast images, to determine parameters such as brightness and contrast of the display.
4. Observe test images or high-quality images and videos to evaluate the color saturation and accuracy of the display.
Therefore, we can’t simply convert 72% NTSC to 100% sRGB, we still have to look at the actual measurement data before we can draw a conclusion.